(+)분류 : 연구실(bwlee42)
1. 합성함수 그래프 그리기 ✎ ⊖
1.1. 개요 및 코드 ✎ ⊖
matplotlib.animation을 통해 합성함수 그래프를 그려보자.
합성함수가 그려지는 과정을 시뮬레이션으로 쉽게 알아보자는 목적으로 만들었다.하지만 볼 사람이 아무도 없을 것으로 예상된다
파일명은 function composition 줄여서 fc로 했고, _(숫자)는 버전이다.
코딩은 직접 할 시간 없어서사실 능력도 안 된다 챗지피티한테 맡겼다.
프롬프트는 내가 직접 짰다.
프롬프트는 잘 알아먹는데, 에러 로그는 잘 못 잡는다. 어느정도 타협하고 만들었다.
합성함수가 그려지는 과정을 시뮬레이션으로 쉽게 알아보자는 목적으로 만들었다.
파일명은 function composition 줄여서 fc로 했고, _(숫자)는 버전이다.
코딩은 직접 할 시간 없어서
프롬프트는 내가 직접 짰다.
프롬프트는 잘 알아먹는데, 에러 로그는 잘 못 잡는다. 어느정도 타협하고 만들었다.
fc_7.py(누르면 펼쳐짐)
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation
def start_animation():
f_expr = f_entry.get()
g_expr = g_entry.get()
if not f_expr or not g_expr:
messagebox.showerror("Error", "f(x)와 g(x)를 모두 입력하세요!")
return
try:
f = lambda x: eval(f_expr, {"x": x, "np": np, "__builtins__": {}})
g = lambda x: eval(g_expr, {"x": x, "np": np, "__builtins__": {}})
except Exception as e:
messagebox.showerror("Error", f"함수 입력 오류: {e}")
return
# x값 범위
x_vals = np.linspace(-3, 3, 200)
# f, g(f(x)) 전체 계산
f_all, gf_all = [], []
for x in x_vals:
y_f = f(x)
if not isinstance(y_f, (list, tuple, np.ndarray)):
y_f = [y_f]
f_all.extend(y_f)
gf_all.extend([g(y) for y in y_f])
f_all = np.array(f_all)
gf_all = np.array(gf_all)
# ---------------------------
# 애니메이션 패널
# ---------------------------
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1,3,figsize=(15,4))
# f 패널
axes[0].plot(x_vals, [np.mean(f(x)) if isinstance(f(x),(list,tuple,np.ndarray)) else f(x) for x in x_vals], color='lightblue')
axes[0].set_title('f(x)')
axes[0].set_xlabel('x')
axes[0].set_ylabel('f(x)')
dot_f, = axes[0].plot([],[], 'ro')
trail_f, = axes[0].plot([],[], 'b', lw=2)
axes[0].set_xlim(min(x_vals), max(x_vals))
axes[0].set_ylim(min(f_all)-0.5, max(f_all)+0.5)
# g 패널
g_all_sorted = np.sort(f_all)
g_vals = [g(y) for y in g_all_sorted]
axes[1].plot(g_all_sorted, g_vals, color='lightgreen')
axes[1].set_title('g(y)')
axes[1].set_xlabel('f(x)')
axes[1].set_ylabel('g(f(x))')
dot_g, = axes[1].plot([],[], 'ro')
trail_g_scatter = axes[1].scatter([],[], c=[], cmap='Greens', s=50)
axes[1].set_xlim(min(f_all)-0.5, max(f_all)+0.5)
axes[1].set_ylim(min(gf_all)-0.5, max(gf_all)+0.5)
# h 패널
axes[2].set_title('h(x) = g(f(x))')
axes[2].set_xlabel('x')
axes[2].set_ylabel('h(x)')
dot_h, = axes[2].plot([],[], 'ro')
trail_h, = axes[2].plot([],[], 'r', lw=2)
axes[2].set_xlim(min(x_vals), max(x_vals))
axes[2].set_ylim(min(gf_all)-0.5, max(gf_all)+0.5)
# ---------------------------
# 히스토리
# ---------------------------
x_hist_f, y_hist_f = [], []
x_hist_h, y_hist_h = [], []
trail_g_count = {}
# ---------------------------
# 애니메이션 업데이트
# ---------------------------
def update(frame):
x = x_vals[frame]
y_f_raw = f(x)
if not isinstance(y_f_raw,(list,tuple,np.ndarray)):
y_f_vals = [y_f_raw]
else:
y_f_vals = y_f_raw
y_h_vals = [g(y) for y in y_f_vals]
# f
dot_f.set_data([x]*len(y_f_vals), y_f_vals)
x_hist_f.extend([x]*len(y_f_vals))
y_hist_f.extend(y_f_vals)
trail_f.set_data(x_hist_f, y_hist_f)
# g
dot_g.set_data(y_f_vals, y_h_vals)
for xf,yf in zip(y_f_vals,y_h_vals):
key = (xf,yf)
trail_g_count[key] = trail_g_count.get(key,0)+1
xs,ys,cs=[],[],[]
for (xf,yf),count in trail_g_count.items():
xs.append(xf)
ys.append(yf)
cs.append(min(count,10))
if xs:
trail_g_scatter.set_offsets(np.c_[xs,ys])
trail_g_scatter.set_array(np.array(cs))
# h
dot_h.set_data([x]*len(y_h_vals), y_h_vals)
x_hist_h.extend([x]*len(y_h_vals))
y_hist_h.extend(y_h_vals)
trail_h.set_data(x_hist_h, y_hist_h)
return dot_f, trail_f, dot_g, trail_g_scatter, dot_h, trail_h
ani = FuncAnimation(fig, update, frames=len(x_vals), interval=50, blit=False, repeat=False)
plt.show()
# ---------------------------
# Tkinter GUI
# ---------------------------
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("합성함수 애니메이션")
tk.Label(root, text="f(x) =").grid(row=0,column=0)
f_entry = tk.Entry(root, width=30)
f_entry.grid(row=0,column=1)
f_entry.insert(0,"x**2")
tk.Label(root, text="g(x) =").grid(row=1,column=0)
g_entry = tk.Entry(root, width=30)
g_entry.grid(row=1,column=1)
g_entry.insert(0,"x+1")
start_btn = tk.Button(root, text="Start Animation", command=start_animation)
start_btn.grid(row=2,column=0,columnspan=2,pady=10)
root.mainloop()
1.2. 실행 ✎ ⊖
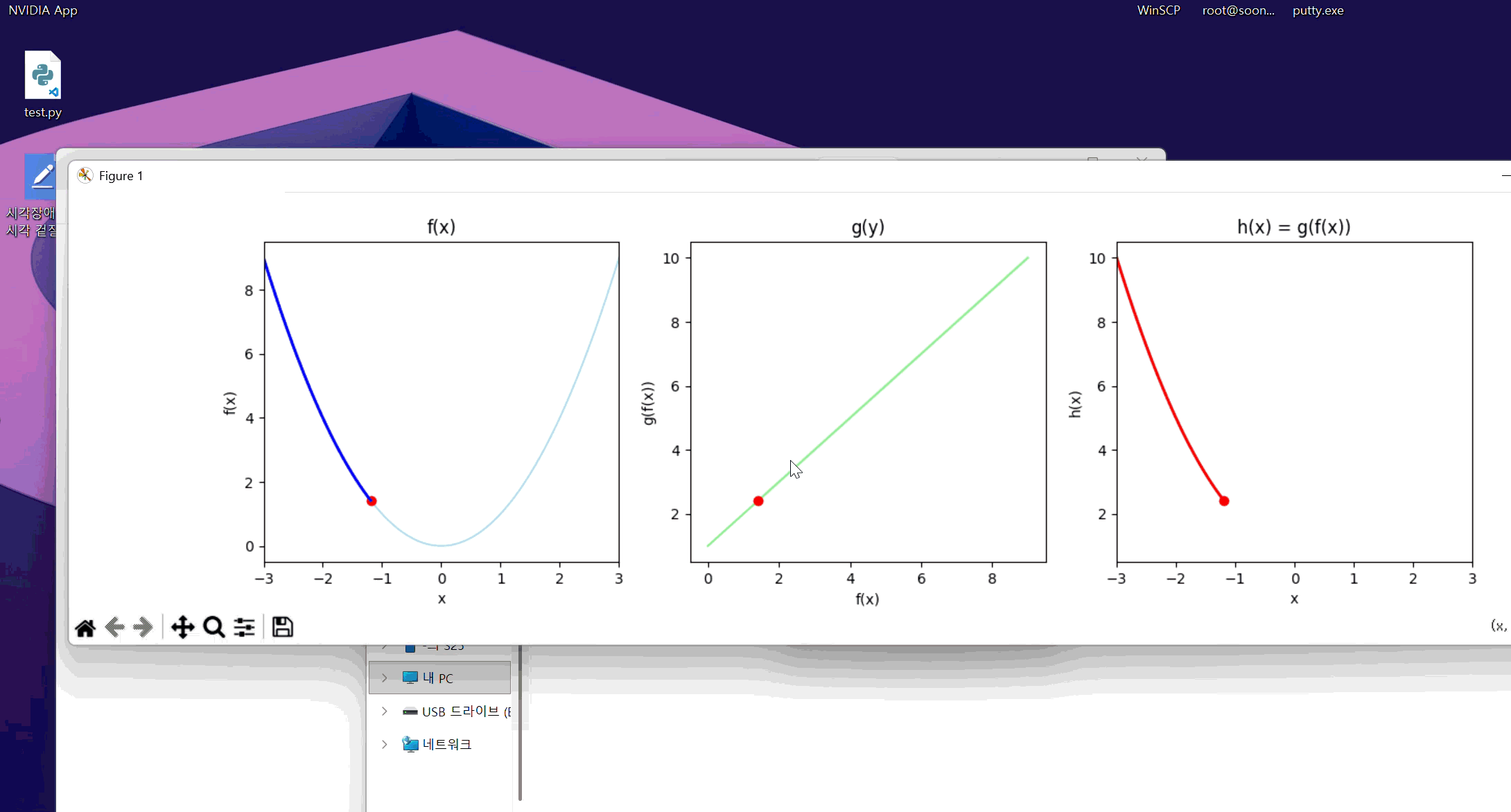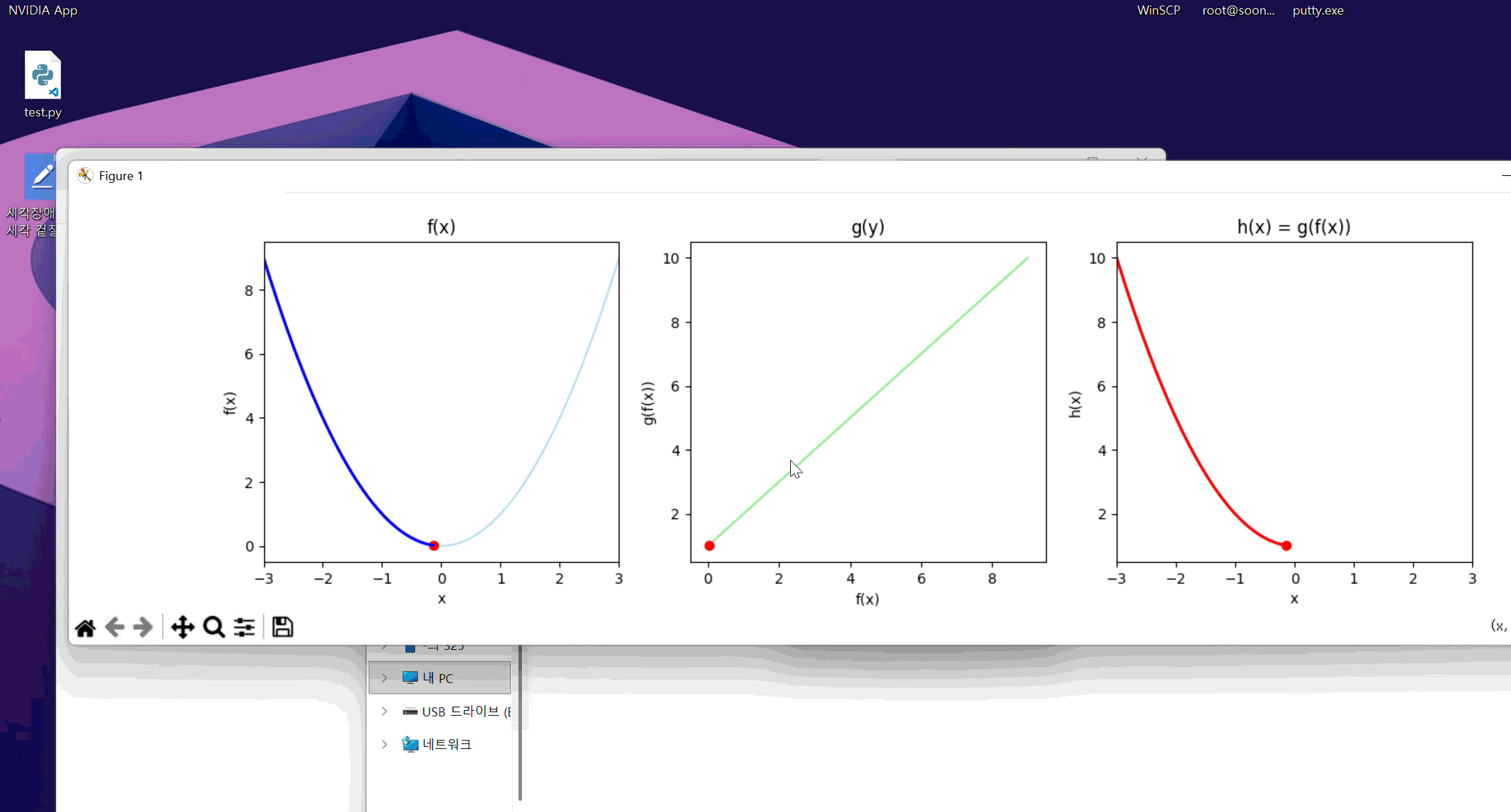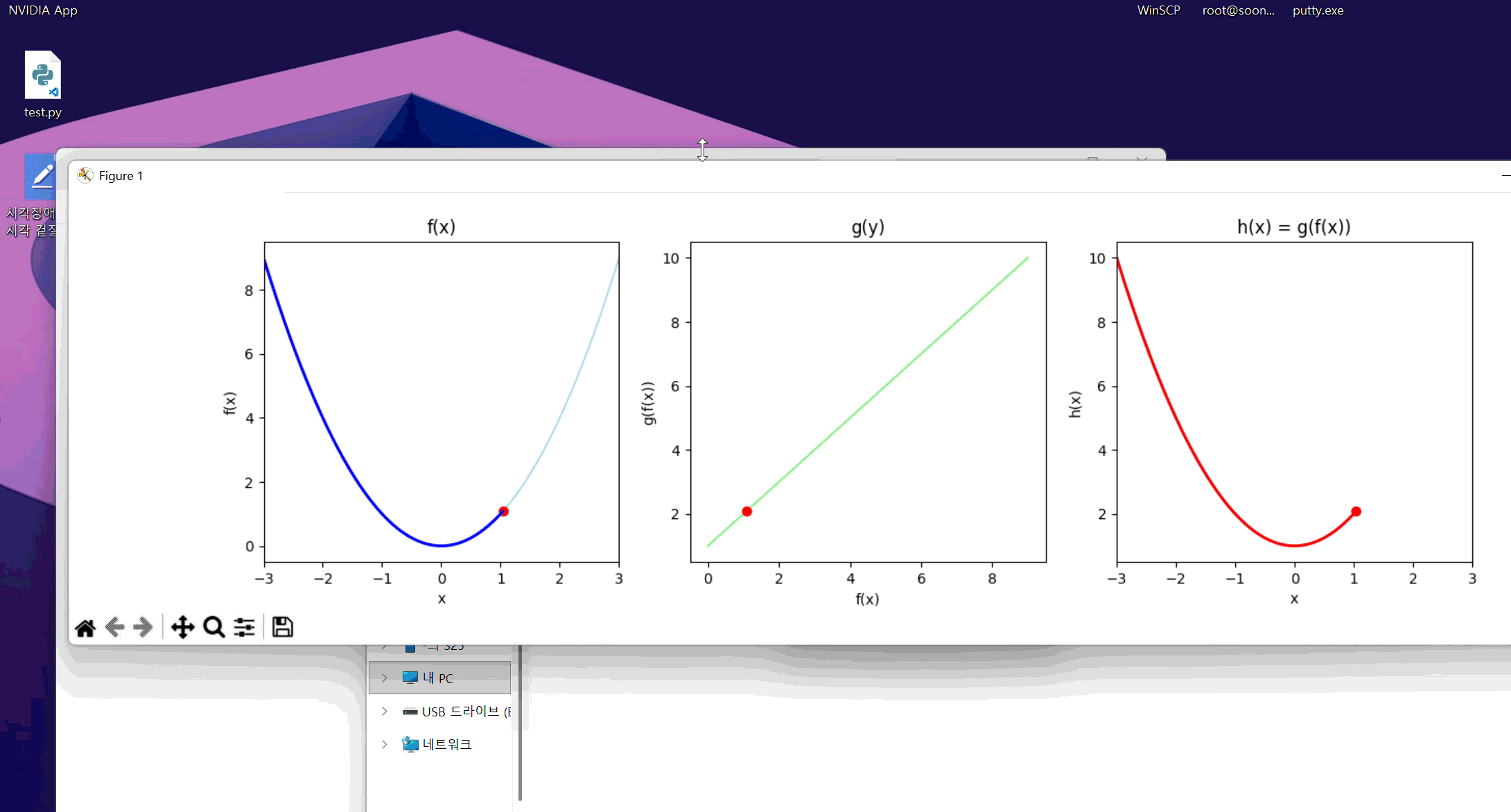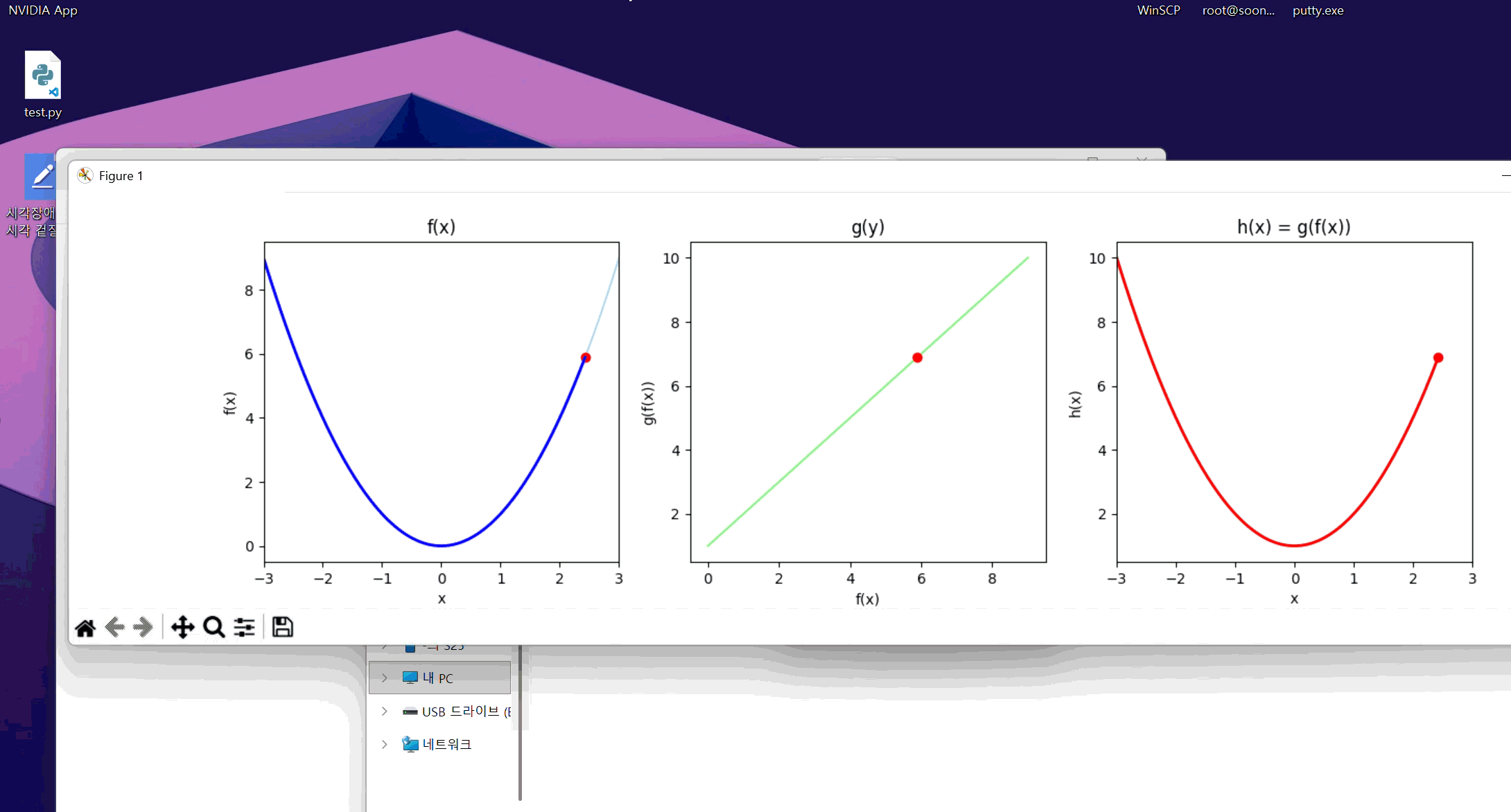
정의역, 공역 표기가 좀 엉망이긴 한데 맨 왼쪽이 f, 가운데가 g, 맨 오른쪽이 f(g(x))이다. 대충 알아먹어라.
f의 치역이 g의 정의역에 대응되어 g의 치역이 h로 그려지는 모습이 보인다.
다시 보려면 창을 새로고침 해라.
파이썬은 비트 XOR 연산자라고 하는 독자적인? 연산자를 사용하기에
| 수학 표기 | 파이썬 입력 | | |
| ----------------
| (x^2) | `x**2` | | |
| (sqrt{x}) | `np.sqrt(x)` | | |
| (sin(x)) | `np.sin(x)` | | |
| (cos(x)) | `np.cos(x)` | | |
| (e^x) | `np.exp(x)` | | |
| (ln(x)) | `np.log(x)` | | |
| ( | x | ) | `np.abs(x)` |
| (1/x) | `1/x` | | |
| (sin^2(x)) | `(np.sin(x))**2` | | |
| (frac{x^2 + 1}{x}) | `(x**2 + 1)/x` | | |
이런식으로 입력해야한다.